FACTS THAT MATTER
Manufacturing is the process of turning basic materials into more valuable goods in big quantities. It helps in the large-scale transformation of raw materials into completed items, resulting in profit, as finished goods are more costly than raw materials.
The development of manufacturing industries in a country is a sign of its economic strength since finished goods are more costly than raw resources.
IMPORTANCE OF MANUFACTURING
- Agriculture can be improved with the help of industrial companies. They support people by giving secondary and tertiary sector jobs.
- Industrial development aids in the reduction of poverty and unemployment in our country.
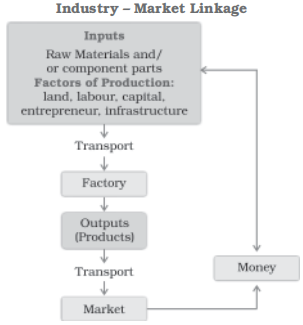
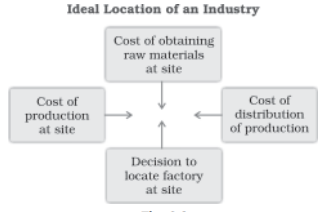
- Several factors determine the location of industries, like access to raw materials, labour, capital, electricity, and market, and many others.
- As a result, manufacturing activity leans toward the most suitable location, where all of the factors of industrial location are either present or can be arranged at a cheaper cost.
- Agriculture and industry are linked. Farmers have been able to increase their output thanks to the development and competition of the manufacturing industry, which has made the production process much more efficient.
CONTRIBUTION OF INDUSTRY TO NATIONAL ECONOMY
During the past two decades, In comparison to some East Asian nations, the manufacturing sector has a vastly lower percentage.
Economists say that manufacturing will meet its target over the next decade if the government makes proper policy reforms and the industry deepens its efforts to improve productivity.
INDUSTRIAL LOCATION
The access to raw materials, labour, capital, power, and markets, among other factors, impact industrial locations.
Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. When industrial activity begins, urbanisation follows. Cities offer the sector with markets and services such as banking, insurance, transportation, labour, consultants, and financial guidance.
CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIES
- Agro-based and mineral-based industries are dependent on raw materials.
- Basic, primary or important industries and Consumer industries are classified based on their main functions.
- Small and big scale industries are classified based on capital investment.
- On the basis of ownership, industries are classified as public, private, joint, or cooperative.
- Heavy and light industries are classified based on the volume and weight of raw materials and finished goods.
AGRO-BASED INDUSTRIES
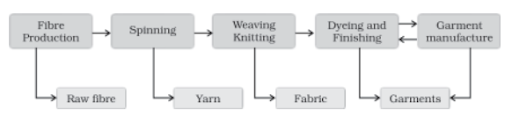
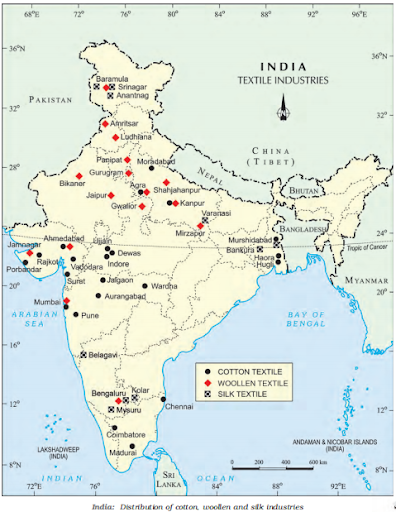
TEXTILE INDUSTRY: It holds a unique place in the Indian economy because it makes a major contribution to industrial production and job creation. India has over 1950 cotton and hand-made fibre textile mills.
India has world-class spinning production, but weaving produces low-quality fabric because it cannot employ most of the country’s high-quality yarn.
COTTON TEXTILE INDUSTRY: It is currently facing a number of issues as a result of unstable electrical supply, old and aged machinery, low labour supply, and fierce competition from the synthetic fibre industry.
JUTE TEXTILES: Near Kolkata, the first jute mill was built. India is now the world’s leading supplier of raw jute and jute products.
Due to the presence of synthetic replacements in the international market, as well as other competitors such as Bangladesh, Brazil, the Philippines, Egypt, and Thailand, the sector faces strong competition.
SUGAR INDUSTRY: India is the world’s second-largest sugar supplier and the world’s first-largest gur and khandsari producer. In the country, there are around 642 sugar mills.
Only Uttar Pradesh has half of India’s sugar mills. However, mills have relocated to the southern and western regions in recent years, particularly Maharashtra.
MINERAL-BASED INDUSTRIES
Minerals and metals are used as raw materials in this industry.
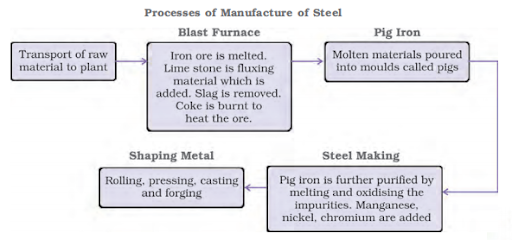
IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY: This is a heavy industry that acts as a foundation for all other industries by providing all forms of machinery needed to run them.
Steel is used to make a wide range of engineering products, construction materials, defence, medical, telecommunications, and scientific equipment, as well as a wide range of consumer goods. Steel production and consumption are used as indicators of a country’s progress.
ALUMINIUM SMELTING: Smelting of aluminium is the second-largest metallurgical sector. Bauxite is a bulky, dark reddish-colored rock that is used in smelters as a substitute for steel,
copper, zinc, and lead in a variety of industries. 
CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES: It is Asia’s third-largest and the world’s twelfth-largest chemical industry. It includes both large and small manufacturing facilities. These enterprises can be found all across the country.
FERTILISER INDUSTRY: India is the world’s third-largest producer of nitrogen-based fertilisers. There are 57 fertiliser manufacturing plants that produce nitrogenous and complex nitrogenous fertilisers.
CEMENT INDUSTRY: Cement is used in the construction of homes, factories, bridges, highways, airports, dams, and other commercial buildings.
Limestone, silica, alumina, and gypsum are all bulky and heavy raw minerals used in this sector.
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY: Automobiles make vehicles that are used to transport goods and passengers quickly. In the past 20 years, this industry has grown at a rapid pace.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY: Transistors, television, telephones, cellular telecom, pagers, radars, computers, and other goods are all part of the electronics sector.
The IT industry has helped to reduce unemployment by hiring a huge number of people.
INDUSTRIAL POLLUTION AND ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION
While fast industrial growth has certainly led to a significant economic growth, it has also resulted in a rise in pollution of land, water, air, and noise, finally resulting in destruction of the environment. Rapid industrialisation in the name of economic progress has resulted in a slew of significant issues.
CONTROL OF ENVIRONMENT DEGRADATION
Reducing environmental degradation should be done in a variety of methods. NTPC, India’s largest power company, has made a number of actions to protect the environment and protect the country’s natural resources.
Outro
NCERT Notes for Class 10 Social Science (Geography) Chapter 6 – Manufacturing Industries
Manufacturing is the process of producing items in big numbers once they have been processed from raw ingredients. Workers at steel mills, automobile manufacturers, breweries, textile mills, and bakeries, for example, are classified as secondary workers. CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 – Manufacturing Sectors focuses on manufacturing industries that are classified as secondary.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science notes will assist students in studying the topic thoroughly and clearly.
These CBSE Class 10 Social Science notes were written by subject experts who made the study material very basic, both in terms of language and format.
NCERT Solved Question Answer CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 06 – Manufacturing Industries
Multiple choice questions.
(a) Which industry uses limestone as a raw material ?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Plastic
(d) Automobile
Answer: (a) Cement.
(b) Which agency markets steel for the public sector plants ?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Answer: (b) Sail.
(c) Which industry uses bauxite as a raw material ?
(a) Aluminium Smelting
(b) Cement
(c) Paper
(d) Steel
Answer: (c) Aluminium.
(d) Which industry manufactures telephones, computers etc.
(a) Steel
(c) Aluminium Smelting
(b) Electronic
(d) Information Technology
Answer: (d) Electronic industry.
What is manufacturing?
Answer: Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials into more valuable goods that can be made in large quantities. For instance, paper is made from wood, sugar is made from sugar cane, steel is made from iron ore, and aluminium is made from bauxite.
- Name any three physical factors for the location of the industry.
Answer: Three physical factors for the location of the industry are as given below :
- Near where the raw materials are.
- Being close to power, or sources of power.
- Climate is important, especially when setting up agricultural businesses like cotton and jute textile
Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
Answer: Three human factors for the location of an industry are as mentioned below :
- Labour – It may be skilled or unskilled.
- Transport facilities –Good transportation is needed to get raw materials to factories and finished goods to the market.
- Demands for goods –There needs to be a demand for goods so that they can be bought and used. Some goods may be made because the people around the industries have enough money to buy them.
What are the basic industries? Give an example.
Answer: Basic industries are those that supply other industries with their products or raw materials. For example, iron and steel, copper smelting, and aluminium smelting are all basic industries.
Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement?
Answer: Limestone, silica, alumina, and gypsum are all important raw materials that are used to make cement.
(1) How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants? What problems does the industry face? What recent developments have led to a rise in production capacity?
Answer:
(1) Integrated steel plants are large.
- They do everything in one complex, from gathering raw materials to making steel and rolling and shaping it.
- From alloy to steel, these plants make it all.
(2) Mini Steel Plants :
- Mini steel plants are smaller, use scrap steel and sponge iron, and have electric furnaces.
- They also have re-rollers that use steel ingots. They make mild steel and alloy steel that meets certain standards.
(3) The following problems are being faced by this industry —
- Coking coal is expensive and hard to get.
- Less work getting done, inconsistent energy supply, and bad infrastructure.
(4) Liberalisation and Foreign Direct Investment have led to a rise in the production capacity of steel industry. Efforts of private entrepreneurs have given a boost to the industry. However, there is a need to allocate resources for research and development to produce steel more competitively.
(2) How do industries pollute the environment?
Answer: Industries have increased pollution and degraded environment. Industries create four types of pollution, namely, air, water, thermal and noise.
These are explained as given below:
Air pollution: The smoke emitted by til’s industries pollute air and water badly.
- Air pollution happens when there are a lot of bad gases in the air, like sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- There are both solid and liquid particles in the air, like dust, sprays, mist, and smoke.
- Chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries, and smelting plants, as well as large and small factories that don’t follow pollution rules and burn fossil fuels, all put out smoke.
- The gas leaks can be very dangerous and cause problems for a long time. For example, the Bhopal Gas Tragedy killed hundreds of people and hurt the health of humans, animals, plants, and other living things as a whole.
Water pollution :
- Both organic and inorganic wastes from factories are dumped into rivers. They make the water bad.
- Some of the most common things that pollute water are coal, soaps, pesticides, and fertilisers.
- Paper, pulp, textiles, chemical, petroleum, and electroplating are the main industries that pollute water.
- Pesticides, dyes, detergents, acids, salts, and heavy metals like lead and mercury are dumped into water bodies by these industries.
- India’s biggest solid wastes are fly ash, phosphogypsum, and iron and steel slags.
Thermal pollution :
- Thermal pollution happens when hot water from factories and thermal plants is dumped into rivers and ponds before it has cooled.
- Nuclear power plants, nuclear weapons factories, and other places that make nuclear waste cause cancer, birth defects, and miscarriages.
- Putting trash on the ground, especially glass, harmful chemicals, industrial waste, packaging, salt, and trash, makes the soil useless.
- Rainwater seeps into the ground and brings pollution with it. This pollutes the groundwater as well.
Noise pollution :
- Machinery, factory equipment, generators, saws, and other tools, as well as construction and industrial activities, make a lot of noise that is bad for people.
- It can hurt your hearing, speed up your heart rate, and raise your blood pressure, among other things.
- Unwanted noise can be annoying and cause stress.
(3) Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry?
Answer: Some suggestions to minimise environmental degradation are given below :
- To use as little water as possible for processing by using and recycling it in two or more steps.
- Getting enough water by collecting rainwater.
- Before putting hot water and waste water into rivers and ponds, they are cleaned.
- Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases as given below:
- The first treatment is done with machines. This is done by sorting, grinding, clumping, and settling.
- Biological processes are used for secondary treatment.
- Biological, chemical, and physical processes are used for tertiary treatment. This means recycling water that has been used.
- There should be careful planning, careful placement of industries, better equipment design, and better use of the equipment.
- The taking of too much water from groundwater reserves should be against the law.
- Particles in the air can be reduced by putting electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers, and inertial separators on factory smoke stacks.
- By using oil or gas instead of coal in factories, smoke can be cut down.
- You can use machinery and equipment, and generators should have silencers added to them.
- Almost all machinery can be changed to use less energy and be quieter.
- Aside from earplugs and earphones, noise-blocking materials can be used in other ways.
Give one word for each of the following with regard to industry. The number of letters in each word are hinted in brackets.
Answer:
(i) Power
(ii) Worker
(iii) Market
(iv) Retailer
(v) Product
(vi) Manufacture
(vii) Pollution.
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
- Textiles, sugar, vegetable oil and plantation industries deriving raw materials from agriculture are called.
- The basic raw material for sugar industry.
- This fibre is also known as the ‘Golden Fibre’.
- Iron-ore, coking coal, and limestone are the chief raw materials of this industry.
- A public sector steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
- Railway diesel engines are manufactured in Uttar Pradesh at this place.
Answer:
- Agro-based
- Sugarcane
- Jute
- Iron Steel
- Bhilai
- Varanasi.